CertAlert Technical Specifications
Comprehensive certificate management solution for enterprise environments
What is CertAlert?
CertAlert is an enterprise-grade .NET application designed for comprehensive SSL certificate management. It thoroughly scans your networks based on configured IP ranges (or hostnames) and port ranges, generating detailed CSV and summary PDF reports on all discovered certificates.
CertAlert excels at identifying certificate issues critical to enterprise security, including expired certificates, approaching expirations, self-signed certificates, weak algorithms (like MD5), and insufficient key lengths. Beyond just displaying progress in a PowerShell command window, CertAlert can deliver alerts and reports via email to designated team members and stakeholders, ensuring timely certificate renewal.
Whether run manually from a command window or scheduled to execute periodically using the Windows Task Scheduler, CertAlert provides the enterprise-grade certificate monitoring your organization needs.
Prevent Costly Outages
Receive timely alerts when certificates need renewal, preventing unexpected service disruptions that impact operations and revenue
Increase Efficiency
Save valuable time by automating certificate discovery and monitoring across your entire network infrastructure
Reduce Costs
Lower your certificate management overhead and eliminate the expense of emergency fixes for expired certificates
Maintain Trust
Protect your brand reputation by preventing the security warnings and errors caused by expired certificates
- Network Discovery: Scan by IP ranges or hostname lists
- Multi-Platform: Identify certificates on Windows, Linux, Unix, and network devices
- Configurable Scanning: Customize ports and port ranges
- Comprehensive Support: All certificate types (OV, DV, EV, self-signed)
- Expiry Monitoring: Automated alerts to multiple recipients
- Detailed Reporting: CSV and PDF with configurable fields
- Security Analysis: Detect issues with issuers, key lengths, and algorithms
- Protocol Coverage: HTTPS, LDAPS, POP3S, IMAPS, SMTPS
- STARTTLS Support: For SMTP certificates
- Task Automation: Schedule with Windows Task Scheduler
Each time CertAlert runs, it generates two comprehensive reports: a detailed CSV report and a summary PDF report. The PDF highlights specific certificate issues such as self-signed certificates, certificates with weak keys, and those using outdated algorithms like MD5.
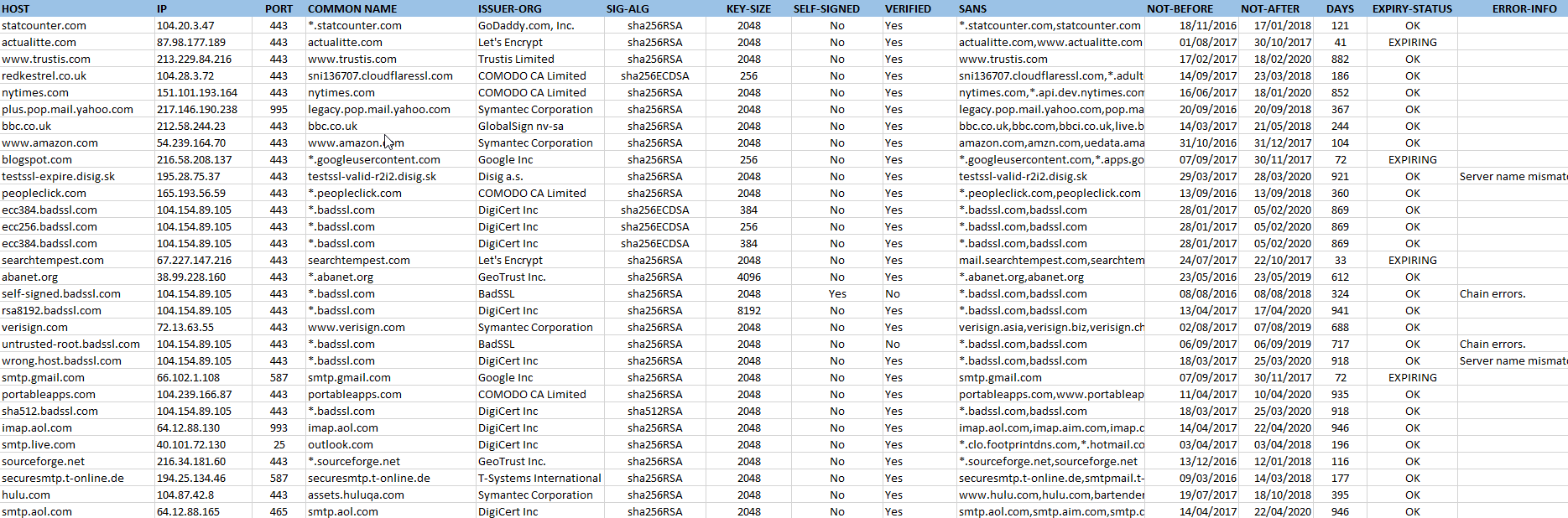
The CSV report contains extensive data about all certificates found, enabling detailed analysis and integration with other enterprise systems. Below are examples of both report types:
CertAlert's reporting system is highly configurable, allowing you to include the certificate data most relevant to your organization. The table below describes the available fields that can be included in your CSV reports:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Hostname | A hostname (if available) indicating the target host |
| IP | An IP indicating the target host |
| Port | The TCP port used to communicate with the remote server |
| Common Name | The Common Name (CN) of the server's certificate, typically matching the fully qualified domain name |
| Issuer Org. | The organisation part of the issuer's distinguished name |
| Issuer | A distinguished name defining the entity that issued the certificate |
| Subject | A Distinguished Name defining the entity associated with the certificate |
| Sig-Alg | The signature algorithm used to sign the certificate (identifies insecure algorithms like MD5) |
| Key-Size | The key size in bits |
| Serial-Number | The certificate's serial number |
| Self-Signed | Indicates if the certificate is self-signed |
| Verified | Indicates if the certificate was verified in line with RFC 5280 |
| SANS | The certificate's DNS subject alternative names |
| Not-Before | The date the certificate becomes valid |
| Not-After | The date after which the certificate is no longer valid |
| Days | The number of complete days before the certificate expires |
| Expiry-Status | One of the following: OK, EXPIRING, EXPIRED, ERROR |
| Certificate | The complete certificate in PEM format |
| Error-Info | Information about errors that occurred when getting or validating the certificate |
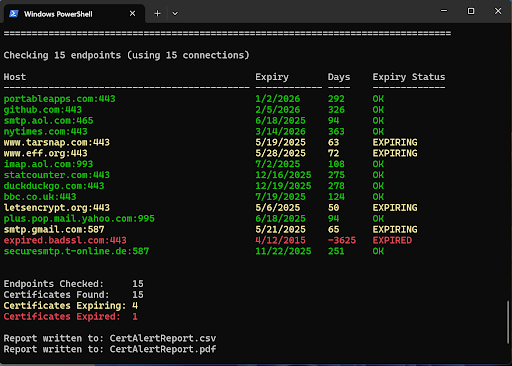
The screenshot shows CertAlert's console output during operation. CertAlert can be run manually as shown or automated through Windows Task Scheduler for continuous monitoring.
To get started with CertAlert, visit our Getting Started page for step-by-step instructions on downloading and configuring the application for your environment.
Security Note
CertAlert runs locally within your secure environment—no certificate data leaves your network unless you choose to send reports externally.
SSL certificates, like identity documents, have a fixed validity period. Certificate Authorities (CAs) include an expiration date when issuing certificates, typically one to two years from issuance. Maintaining valid certificates requires renewal before expiration.
For organizations managing numerous certificates with different expiration dates from multiple CAs, this process can become complex and error-prone. CertAlert mitigates this risk by systematically scanning your servers and providing advance alerts when certificates approach expiration.
Whether configured with IP ranges or hostname lists, CertAlert thoroughly monitors certificate status across your environment. It generates comprehensive CSV reports suitable for importing into spreadsheets or databases, provides real-time console feedback, and delivers customizable email alerts to designated recipients.
For additional information, please see our CertAlert FAQ or contact our support team at [email protected]
Ready to secure your certificate infrastructure?
Get started with CertAlert today and prevent costly certificate-related outages.
Download Now